Contents
- Coenzyme-Q10 Reduced CoQ10, Ubiquinol, Ubiquinone)
- L-Citrulline
- L-Glutathione (Reduced Glutathione, GSH)
- L-Arginine
- D-Aspartic Acid (DAA)
- L-Tyrosine
- ALCAR (Acetyl-L-Carnitine)
- BCAA (Branched-Chain Amino Acids)
- Creatine
- AAKG (Arginine Alpha-Ketoglutarate)
- SAM-e (S-Adenosylmethionine)
- L-Glutamine
- β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (Beta-NMN)
- Nicotinamide Riboside (NR-Cl)
- Resveratrol
- Quercetin
- Rhodiola Rosea
- Maca Root
- Mucuna Pruriens
- Tribulus Terrestris
- Fenugreek Seed
- Butea Superba
- Eucommia
- Phosphatidylserine (PS)
- Ursolic Acid
- L-Ornithine
- Cordyceps Sinensis
- Tongkat Ali
1. Coenzyme-Q10 (Reduced CoQ10, Ubiquinol, Ubiquinone)
Coenzyme-Q10 is a substance found in cells throughout the body, especially in the liver, pancreas, heart, and kidneys. Although, it is a fermented supplement, it is found in small amounts in meat and fish. Coenzyme Q10 is necessary for the functioning of many chemical reactions and organs in the body.

Coenzyme Q10
The essential antioxidant nutrient found in the mitochondria of human cells. The function of mitochondria is specifically related to the production of the energy our bodies need, commonly known as ATP synthesis. CoQ10 is essential for cellular machinery to extract energy from lipids and carbohydrates. In addition, Coenzyme Q10 can also increase the absorption of other essential nutrients by recycling vitamins C and E.
It is frequently prescribed for a number of ailments, including heart failure, hypertension, blood infections, blood poisoning, periodontal disease, migraine headaches, muscular weakness (mitochondrial myopathies), diabetic neuropathy, fibromyalgia, and Parkinson’s disease. Additionally, coenzyme Q10 levels may fall as we get older and become inadequate.
Benefits
Cellular energy. Coenzyme Q10 is essential for cellular energy generation, also known as ATP synthesis. There is some proof it can relieve weariness after exercise.
Free radicals. The functional deficits associated with aging and disease are significantly influenced by oxidative damage to cell components. Our cells experience significant stress as we age due to the oxidative damage induced by free radicals. Heart disease, diabetes, neurological disorders, and some types of cancer are all partially caused by oxidative damage, which coenzyme Q10 acts as a first line of defense against.
Cardiovascular disease. Preventing heart disease is another intriguing CoQ10 impact. Not only do statins lower liver cholesterol levels, but they also reduce the amount of coenzyme Q10 the liver produces. There is some scientific support for how raising CoQ10 levels can help people taking statin medications with their blood pressure and coronary artery disease.
Aging and longevity. We know that as we age, our levels of coenzyme Q10 decrease. It’s levels are decreased not only in skin tissue but also in interior organs like the heart, liver, and muscles. Coenzyme Q10 has the potential to be helpful in topical lotions and serums, preserving a healthy liver metabolism, and shielding the heart from the damaging effects of free radicals.
Maintaining pH levels. Numerous diseases, including malignancies, seem to spread more quickly in conditions where cells’ ideal pH levels are not maintained. Additionally, there are some encouraging findings about the speed of recovery when adding CoQ10 to cancer treatment medications.
Cognitive decline. Studies have found that people with age-related cognitive decline have lower Coenzyme Q10 levels. For example, in patients with Parkinson’s disease, a specific region of the brain called the substantia nigra is particularly affected as the disease progresses. CoQ10 is thought to balance the effects of oxidative stress in brain regions.
Male infertility. There is some scientific evidence that supplementing with CoQ10 can improve male fertility. In particular, effects on sperm count, sperm motility, and egg fertilization rates were observed.
Treatment for fibromyalgia. As evidenced by improvements in cholesterol levels as well as self-reported complaints of fatigue, headaches, and muscular and joint pain, Coenzyme Q10 appears to have multiple positive impacts on fibromyalgia.
Side-effects
Coenzyme Q10 is generally well tolerated but can cause mild side effects such as upset stomach, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, and rash. It also lowers blood pressure, so check yours. Splitting the total daily dose by taking 2-3 smaller doses per day can help reduce side effects. Not enough is known today about the use of CoQ10, so it is better to avoid it during a pregnancy.
2. L-Citrulline
L-Citrulline is an amino acid that can be found naturally in some foods, such watermelons, and is also synthesized by the body. Like alanine, arginine, and glycine, it is regarded as non-essential, which implies the body is capable of producing it on its own.
L-citrulline is changed by the body into L-arginine, an additional amino acid, as well as nitric oxide chemistry. Along with nitric oxide supplements that increase nitric oxide levels in the body, it also acts as a vasodilator to relax blood vessel muscles, increase blood flow, and lower blood pressure. As a result of its capacity to encourage healthy blood flow, it has been linked to a number of potential health advantages. In fact, it is believed to lower blood pressure, prevent erectile dysfunction, and promote oxygen uptake to improve exercise performance.
Benefits
Enhancing exercise performance. It may be helpful to take citrulline by mouth to enhance some forms of exercise performance. L-citrulline may be used orally to improve various types of exercise performance. Some athletes may work harder, continue lifting weights longer, and pedal an exercise bike more quickly when using L-citrulline. According to some research, this amino acid may assist the muscles better utilize oxygen, which is very advantageous for your exercise regimen.
For instance, a study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Medicine indicated that taking a supplement containing citrulline increased cyclists’ physical performance and even reduced their post-exercise fatigue and lack of focus. The results of the study demonstrated that boosting oxygen uptake improved endurance and the effectiveness of high-intensity exercise.
Heart disease. People with heart failure who are currently on generic medications may benefit from taking L-citrulline. In these patients, taking L-citrulline orally has a tendency to reduce pulmonary blood pressure. People with heart problems can walk more quickly thanks to this improved cardiac function.
Muscle expansion. These kinds of amino acids are critically necessary for building muscles. According to studies, this important substance encourages the synthesis of muscle proteins and is crucial for preserving the homeostasis of proteins. A study conducted in Mallorca, Spain, revealed that ingesting citrulline malate could improve the utilization of branched-chain amino acids during exercise and raise levels of human growth hormone, a protein hormone known to improve physical stamina and muscle strength.
Erection problems (ED). In certain erectile dysfunction (ED) sufferers, oral L-citrulline administration appears to improve sexual performance. Erectile dysfunction, which can be brought on by physical disorders like high blood pressure as well as mental and emotional difficulties like stress, is the inability to get or keep an erection. Citrulline is one of the most popular natural alternatives to pharmaceutical medications because of its capacity to boost blood flow and lower blood pressure levels.
Although this amino acid was not as effective as other ED prescription medications like Sildenafil, according to a 2011 study from the University of Foggia in Italy, it was able to alleviate some erectile dysfunction symptoms after just one month. So how long does L-citrulline take to treat ED? Although individual outcomes may differ, the majority of people report symptom improvements within the first few weeks of beginning supplementation.

Citrulline is found in melons
High blood pressure (HBP). When blood flows from the heart to the lungs under a high blood pressure we call the condition pulmonary hypertension. citrulline supplementation lowers pulmonary blood pressure in the arteries and facilitates greater walking capacity in pulmonary hypertension patients. Citrulline and blood pressure levels have a strong relationship, according to multiple encouraging studies. It has been demonstrated to act as a typical nitric oxide booster and assist in enhancing the function of blood vessel-lining cells.
According to a study from Japan, taking a supplement containing citrulline increased endothelial dysfunction and lowered lipoprotein oxidation, both of which can result in atherosclerosis or fatty plaque buildup in the arteries. Another study found that ingesting this amino acid reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure by 6% and 14%, respectively, and was published in the European Journal of Applied Physiology.
Sickle cell disease. By ingesting citrulline orally, sickle cell disease sufferers may see some symptom improvement.
Side-effects
Although adverse effects are uncommon, some persons who take citrulline by mouth have complained of stomach discomfort, heartburn, coughing, changes in urine, and edema. To determine whether taking L-citrulline while pregnant or breast-feeding is safe requires a sufficient amount of trustworthy scientific data.
3. Glutathione
Reduced L-Glutathione (GSH) is an antioxidant that is made by cells in the human body, but that can also be found in many fruits, vegetables, and meat products. It is made up by combining three amino acids: glutamine, glycine, and cysteine. The body uses it for a variety of tasks, including immunological function, protein synthesis, immune system support, and tissue maintenance and repair. A number of things, including poor nutrition, pollutants in the environment, stress, and age, can cause the levels of the antioxidant to fall.
Numerous health issues are treated with glutathione, including aging, alcoholism, asthma, cancer, heart disease (atherosclerosis and high cholesterol), hepatitis, liver disease, illnesses that impair the body’s immune system (AIDS, chronic fatigue syndrome), memory loss, Alzheimer’s disease, osteoarthritis, Parkinson’s disease, and male infertility. Glutathione is largely used to treat drug and metal poisoning and to maintain the body’s immune system.
Benefits
Decreasing Oxidative Stress. When the body’s capacity to combat free radicals and their creation are out of balance, oxidative stress results. Excessive oxidative stress may be a risk factor for a number of diseases. These include diabetes, cancer, and rheumatoid arthritis. Glutathione helps to reduce the adverse effects of oxidative stress, which may minimize the risks for illness. One study found that shortages lead to greater levels of oxidative stress, which may result in cancer. Additionally, it was mentioned that higher glutathione levels increased antioxidant levels and cancer cell resilience to oxidative stress.
May reduce symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s disease is a central nervous system disorder that is characterized by tremors and other symptoms. There isn’t a treatment for it as of now. An older study documented the positive effects of intravenous glutathione on symptoms such as tremors and rigidity. Although additional research is required, it appears that glutathione may help Parkinson’s patients live better lives and experience less symptoms.
May support defence against autoimmune diseases. Oxidative stress can be exacerbated by the persistent inflammation brought on by autoimmune illnesses. These illnesses include lupus, celiac disease, and rheumatoid arthritis. According to one study, glutathione either increases or decreases the body’s immune response, which helps alleviate oxidative stress. While autoimmune diseases attack the mitochondria in specific cells, glutathione works by scavenging free radicals and protecting the mitochondria of cells.
May reduce oxidative damage in children with autism. May lessen oxidative damage in autistic kids. Numerous studies have found that the brains of children with autism exhibit higher levels of oxidative damage and lower levels of glutathione. This makes autistic children more vulnerable to neurological damage from chemicals like mercury. Glutathione was administered orally or topically to children aged 3 to 13 during an eight-week clinical study. The study did not assess changes in autistic symptoms, although children in both groups had higher levels of cysteine, plasma sulfate, and whole-blood glutathione.
Increased mobility in peripheral artery disease. When the peripheral arteries get blocked by plaque, which mainly occurs in the legs, peripheral arterial disease occurs. According to one study, glutathione boosted circulation and the individuals’ capacity to walk pain-free over longer distances. Instead of a saline placebo, glutathione was administered intravenously to participants twice daily for five days.
Improved insulin resistance in older people. As people age, they produce less glutathione. In one study, the impact of glutathione on elderly people’s insulin resistance and weight control was investigated. According to the research, low levels of glutathione were linked to lower rates of fat burning and higher rates of fat storage in the body. Subjects then had cysteine and glycine added to their diets to increase glutathione levels, which spiked within two weeks and improved insulin resistance and fat burning.
May improve psoriasis. A small trial found that oral administration of whey protein reduced psoriasis without the need for additional therapy. It has already been shown that whey protein raises glutathione levels. The trial lasted for three months, during which the subjects received an oral supplement of 20 grams each day. More research is necessary to verify the effect.
May reduce impact of diabetes. Low levels of glutathione are related to chronic high blood sugar. Tissue damage and oxidative stress may result from this. According to one study, adding cysteine and glycine to the diet increased the amounts of glutathione in the body. Despite having elevated sugar levels, it reduced oxidative stress and damage in uncontrolled diabetes. For two weeks, subjects were given 0.81 mmol of cysteine and 1.33 mmol of glycine per kilogram each day.
Reduced cell damage from to fatty liver disease. As glutathione is the key antioxidants in the body, the deficiency may exacerbate liver cell death. Both those who abuse alcohol and people who do not have fatty liver disease may get it as a result. Protein, enzyme, and bilirubin levels in the blood of people with alcoholic and nonalcoholic chronic fatty liver disease have been demonstrated to be improved by glutathione. According to one study, intravenous administration of high doses of glutathione to patients with fatty liver disease had the best results. Malondialdehyde, a measure of liver cell damage, decreased in research participants as well.
May reduce respiratory disease symptoms. Asthma and cystic fibrosis are two illnesses that are treated with N-acetylcysteine. It helps mucus become thinner and less paste-like when breathed.
Side-effects
Side effects of glutathione supplements are usually mild, but taking it may not be suitable for all people. If you want to know if it’s appropriate for you, speak with your doctor. Constipation, bloating, difficulty breathing (bronchial constriction), and allergic responses are possible side effects.
4. L-Arginine
Despite the fact that L-Arginine is a non-essential amino acid, it is conditionally essential, because it is necessary for a number of processes and is typically present in small amounts. The ability of arginine to increase blood flow and respiration is one of its main benefits. It is changed by the body into nitric oxide, which expands blood arteries.
Arginine has various advantages, including improving cognitive function, infertility, lowering blood pressure, detoxification, and immunological function. Additionally, it promotes the production of several hormones, particularly insulin and growth hormones, which help incorporate glucose into cells for growth and energy production. It is thought this is behind the increased physical strength, endurance, and power.
Examining the role nitric oxide (NO) in the body is helpful for understanding how L-arginine works. Reactive natural gas of Nitric Oxide type is produced by both plants and animals. It is a by-product of numerous chemical reactions and is created utilizing the amino acid L-arginine and the nitric oxide synthase. Arginine is able to produce enough nitric oxide to maintain blood flow thanks to the endothelial cells, which line the interior of all blood vessels. Lack of nitric oxide in the arteries increases the risk of heart disease because it worsens circulation by dilating blood vessels.
Research suggests that the ability to produce NOx in the artery linings decreases as someone grows older, which can be remedied with supplemental arginine.
Benefits
Improves Heart Health. Research shows that arginine is effective for reducing inflammation and improving the protection of blood vessels and the cardiovascular system, which is why oral arginine is one of the most common supplements recommended by cardiologists. L-arginine supplements can be an effective measure to prevent a heart attack or stroke for people with high risk factors for coronary heart disease.
Arginine improves cardiovascular health in a number of ways, including lowering high cholesterol, preventing high blood pressure, improving stamina, improving blood flow in people with coronary artery disease, and reducing symptoms of congestive heart failure and symptoms of reduced blood flow from the heart to the limbs (called claudication).
Lowers inflammation and fights the effects of aging. In addition to cardiac health, one of the primary benefits of L-arginine is the battle against disease-causing inflammation and improved immune function. Due to its effects on the enzyme called superoxide dismutase (SOD), but also through other antioxidant mechanisms, L-arginine has been found to have substantial free radical-scavenging capabilities. It is frequently used in conjunction with antioxidants, such as vitamin C and omega-3 fish oil supplements, to slow down the aging process and fend off numerous chronic illnesses.
Arginine may even decrease the presence of ammonia in the blood, which is why ammonia is sometimes used to treat people with metabolic problems and urethra damage where ammonia is excreted from the body. Ammonia is a body-produced chemical that degrades proteins and causes tissue necrosis, which can result in inflammatory reactions and cell death.
Boosting exercise performance. L-arginine is known to enhance blood flow efficiently, thereby helping to bring nutrients and oxygen to the muscle and joint tissues. That means more of the exercise’s many advantages, but with less discomfort. In some cases, broken joints or cold hands and feet are even used to improve heat and circulation, especially for people with complications from other health conditions such as reduced blood flow, arthritis or diabetes.
The body also uses arginine to increase human growth hormone, prolactin, and several amino acids — including creatine, L-proline, and L-glutamate. It even improves insulin sensitivity by allowing more glucose to enter cells, similar to how exercise does. The role of arginines in metabolic health is important to build strong muscle tissue, fight inflammation that causes bone and joint pain, repair injuries, and overall functions of the nervous system. There is also evidence that supplementation with L-arginine increases insulin from plasma and helps build stronger muscles even when you rest due to its effects on the capillaries of the body.
Improving immunity and speeding up healing from inflammation. In some patients with diseases, trauma and cancer, low-circulating arginine was found. Some immune suppressor cells (MSCs) are thought to contribute to low levels of blood circulation or arginine insufficiency. Arginine is used with omega-3 fish oils and other supplements to reduce infection risk (especially respiratory infections or lung problems), improve wound healing, and shorten recovery after cancer, illness, or surgery. Additionally, it is applied to burns to enhance protein activity and may even help prevent tooth decay and cavities. While more research is still needed due to the immune-enhancing effects of arginine, it is commonly given to people undergoing chemotherapy or healing from surgeries, viruses and infections (e.g. HIV).

Arginine powder
Treating erectile dysfunction and infertility. L-arginine can assist increase sperm production and motility because studies have shown that it plays a role in the correct cell replication process in addition to promoting blood circulation. People who are struggling with cardiovascular problems linked to low NO levels in the blood are more likely to suffer from erectile dysfunction and fertility problems as an erection involves smooth muscle relaxation caused by nitric oxide. A significant percentage of cases of male infertility-one study suggests 92%-may be treated with arginine in combination with other dilators, antioxidants, or anti-inflammatory drugs (such as pine bark).
Men who are overly stressed may benefit especially from supplements since some study indicates that high stress levels in the sperm production system can lower the content of L-arginine. A combination of L-arginine, L-glutamate, and yohimbine hydrochloride is commonly used in the treatment of ED and appears to work better than L-arginine.
Benefits for women. Even women can experience better reproductive help with L-arginine — doctors sometimes prescribe topical creams that contain this amino acid to help heal sexual problems and treat infertility naturally in both sexes as it improves the circulation of genital tissue. However, some research suggests that combined treatment with N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) and arginine may help regulate hormones naturally and restore normal sexual function in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and estrogen imbalances. Many studies suggest that L-arginine used with herbs such as chasteberry, green tea extract and supplements with antioxidants increase pregnancy rates in women trying to conceive.
Side-effects
Even if L-arginine is generally safe, consideration should be given to some potential side effects. If you have a history of heart disease, low blood pressure, diabetes, kidney problems or an infectious infection (such as herpes or shingles), supplementing with L-arginine is not recommended until you first talk to a doctor.
In general, it is still possible to develop short-term side effects, such as abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, gout, developing allergies or asthma and low blood pressure if you are usually healthy and take the dose around a gram daily. Arginine can cause allergic reactions or increased swelling in the pulmonary and respiratory system to cautiously take L-arginine by people with existing allergies or asthma. Last but not least, although there is not much data on the effects in these populations, it is better to stick to a modest dose or consult your doctor first. L-arginine appears safe for pregnant women and even toddlers.
5. D-Aspartic Acid (DAA)
Acidic amino acids are frequently thought of as the foundation of proteins. One of the amino acids that are not required is aspartic acid. L-aspartic acid, like other amino acids, is produced by the human body and serves as a building block for proteins. However, the mirrored counterpart D-Aspartic Acid, commonly known as DAA, contributes to the development of hormones and the function of the nervous system. While numerous research have examined whether D-aspartic acid improves exercise response, it is still unclear whether supplementing with D-aspartic acid increases testosterone levels, endurance, or muscle mass.
Benefits
May increase testosterone. According to certain studies, testosterone levels can be raised by D-aspartic acid in two different ways. It can increase the creation and release of testosterone in the testes as well as release a hormone in the brain that ultimately results in the production of testosterone. An examination of the effects of supplementing with DAA for 12 days in healthy young men revealed that, at the conclusion of the trial, 20 of the 23 participants had greater levels of testosterone (average 42 percent increase).
In a different study, overweight and obese males who took D-aspartic acid experienced increases in testosterone levels (over 20%) compared to those who started out with lower levels. In a third study, men aged 27 to 43 who took D-aspartic acid for 90 days experienced a rise in testosterone of 30 to 60 percent. This study looked at the effects of taking such supplements over the course of a month.
May increase male fertility. Additionally, their partners’ pregnancies have increased. D-aspartic acid supplements were found to significantly improve the amount of sperm that 60 men with reproductive issues generated for three months in one study. Additionally, their sperms motility – or capacity for movement – was enhanced. These increases in sperm quantity and quality appear to have been profitable. The number of pregnancies among the men’s partners who took DAA increased throughout the research. Researchers discovered that utilizing D-aspartate for 90 days raised the likelihood of their spouse becoming pregnant during the test by 27%.
May elevate hormone levels. The amino acid D-aspartic acid is crucial for the production and release of hormones. It makes it easier to regulate a variety of bodily functions, such as blood pressure, sleep patterns, the creation of ATP energy, reproduction, digestion, and adjustments to appetite and metabolism. You can try to naturally balance your hormones by consuming aspartic acid-rich foods. DAA may contribute to a rise in hormone production by building up in the pituitary and the testes.
Side-effects
An extensive blood testing study that looked at the impact of consuming 2.6 grams of DAA per day for 90 days in one study came up empty-handed. On the other side, a smaller study discovered that two out of ten males who took D-aspartic acid complained of irritability, headaches, and anxiousness.
6. L-Tyrosine
L-Tyrosine is necessary for creation of the neurotransmitters epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine, dopamine, and thyroid hormone all depend on the non-essential amino acid l-tyrosine. Moreover, L-tyrosine supports healthy glandular function and stress response.
Tyrosine is frequently used to enhance memory, focus, and alertness under pressure. The body uses tyrosine to make chemical messengers that are involved in conditions involving the brain such as mental alertness. L-tyrosine advantages may include preventing weight gain, depression, weariness, and impaired cognitive function overall.
Benefits
Possibly enhance mental performance and focus. Tyrosine supplements affect mental performance under pressure, according to research. These include stress caused by the cold or stress caused by noise.
May help to improve memory. Tyrosine supplements have been shown to enhance memory under pressure. These include cold-induced stress or multi-tasking. One study found that tyrosine significantly enhanced accuracy and decreased frequency of list retrieval on the working memory task during the multiple task battery.
Improve alertness following loss of sleep. People who have missed a night of sleep can stay alert for an additional three hours by taking tyrosine. Additionally, preliminary research suggests that tyrosine improves memory and thinking in those who are sleep-deprived. There is some proof that increasing your tyrosine intake can enhance your mood, alertness, stress-coping skills, and general cognitive performance. According to one study, it is helpful when soldiers are subjected to physical stressors, such as those that are relevant to the military, such exposure to cold stress, high-altitude stress, or prolonged wakefulness.
May help for depression. Tyrosine affects dopamine and adrenaline levels, which control your reward and pleasure centers and your “fight-or-flight response” under stress, respectively. Catecholamines are released more readily in stressful situations, which may lower their concentrations. Tyrosine can aid in restoring the levels. People who are under a lot of stress or who are depressed may find that increasing their intake of this amino acid is beneficial because symptoms like irritability, weariness, and moodiness tend to worsen when dopamine and norepinephrine levels fall.
May support weight loss. No particular research have been done, according to University of Michigan Medicine, to prove that L-tyrosine aids in weight loss promotion. However, there is some evidence that it may aid in fat loss in overweight individuals when combined with other naturally occurring fat-burning chemicals like cayenne, green tea, and caffeine, but only modestly. In a 2007 study, overweight persons who also took tyrosine, capsaicin, catechins, and caffeine saw a very slight weight loss of about 0.9 kg.
May help for withdrawal symptoms. Dopamine fluctuations have been shown to make people more susceptible to addictions. Low levels might make it difficult to start or finish work, cause sadness, impair focus, sap your energy, and make you unmotivated. Alcohol, drug usage, smoking, gambling, and overeating are examples of addictive habits. Tyrosine, when combined with the medicine naltrexone, may help manage the symptoms of alcohol and heroin withdrawal as well as reduce alcohol consumption, according to ongoing study.
Tyrosine, 5-hydroxytryptophan (HTP), phosphatidylcholine, and L-glutamine appear to have the greatest positive benefits on mood and sleep in individuals addicted to heroin and alcohol, possibly because they assist balance catecholamine levels.
Side-effects
When used by adults as a medication, either temporarily or topically, tyrosine is probably safe. When consumed orally (in amounts up to 150 mg/kg per day for up to 3 months), tyrosine appears to be safe. Some people report having adverse symptoms like heartburn, fatigue, nausea, and headaches. Tyrosine use during pregnancy and breast-feeding is not known to be safe at this time due to a lack of information. Tyrosine supplementation may lead to an excessive rise in thyroxine levels, aggravating Graves’ illness and hyperthyroidism.
7. ALCAR (Acetyl-L-Carnitine)
Acetyl-L-Carnitine and L-Carnitine are both converted by the body in to each other, where L-carnitine is non essential amino acid. Acetyl-L-carnitine assists the body in a number of functions, from producing energy, muscle movement, and many other body processes, such the heart and brain function. Acetyl-L-carnitine has been treated such that it may easily cross the blood-brain barrier and is believed to improve brain health and memory.
For a range of illnesses, including Alzheimer’s disease, age-related memory loss, depression, thinking issues linked to alcoholism, thinking issues linked to Lyme disease, and thinking issues linked to very bad liver function, people take acetyl-L-carnitine orally (hepatic encephalopathy). It is also used to treat other conditions such alcohol withdrawal, Down syndrome, bipolar disorder, inadequate brain blood flow following a stroke, cataracts, nerve pain from diabetes, nerve pain from medications used to treat AIDS or cancer, sciatic nerve pain, fibromyalgia, and facial paralysis.
Benefits
Increases endurance. L-carnitine is a crucial component of energy generation, thus many people utilize it to improve energy levels and endurance during bodybuilding and athletic competition. Giving professional soccer players three to four grams of L-carnitine before training was found to increase the amount of time it took for them to become exhausted in a study from Turkey that was published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. Likewise, rats were given L-carnitine in an animal study from India that was published in the journal Wilderness & Environmental Medicine and shown an increase in exercise endurance. For this reason, supplementing with this amino acid may especially benefit endurance athletes, such as long-distance runners, swimmers or cyclists.
Enhancing weight loss. According to several research, taking supplements can actually be a successful approach to accelerate weight loss when used in conjunction with a healthy diet and regular exercise. A study from Iran that examined the findings of nine different trials indicated that adding carnitine to the diet dramatically increased weight reduction and reduced body mass index when compared to a control group. However, the effects of L-carnitine on weight loss may differ, and other research have produced contradictory findings.
For instance, in an Australian trial that was published in the International Journal of Sports Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 36 obese women underwent eight weeks of aerobic exercise while taking either L-carnitine or a placebo. Researchers came to the conclusion that L-carnitine had no effect on either total body mass or fat mass at the end of the investigation. L-carnitine may be effective for certain people, but it is not a panacea. For best results, combine it with regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Preventing muscle damage. This amino acid is a helpful supplement for athletes trying to avoid and mitigate muscle injury in addition to boosting endurance and speeding up weight reduction. In a study from 2014 that was printed in the Asian Journal of Sports Medicine, 21 male athletes were administered L-carnitine or a placebo every day for two weeks before an athletic test. L-carnitine users were discovered to have lower levels of certain indicators that point to muscle injury than the control group.
Amplifying fat-burning. This amino acid not only speeds up weight reduction, but also speeds up fat burning. Overweight subjects in a German study were given a conventional diet with or without the addition of L-carnitine. L-carnitine was discovered to drastically speed up the breakdown of fat after just 10 days. Another study found that raising the amount of carnitine in muscles helped prevent fat growth by raising fat burning and energy expenditure during physical activity, according to a report in the Journal of Physiology.
Boosts brain function. L-carnitine benefits both your body and mind. It’s not simply helpful for your body. In fact, promising research suggests that it may have a positive effect on cognition and brain function. In one Italian study, the University of Catania examined the impact of daily L-carnitine supplementation on participants’ levels of physical and mental weariness. The results were published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. It was discovered to aid lessen fatigue and enhance cognitive function in addition to reducing total body fat mass and increasing muscular mass. Even further research has shown that acetyl-L-carnitine, a different type of L-carnitine, may assist patients with Alzheimer’s disease reverse cognitive loss and restore memory.
Regulates blood sugar. Carnitine supplementation may help to maintain normal blood sugar levels and combat insulin resistance, according to some encouraging findings. The hormone insulin is in charge of delivering bloodstream sugar to cells where it can be used as fuel. Insulin resistance, which reduces its efficiency and causes high blood sugar, can be brought on by an excess of insulin. A study from Rome that was published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition demonstrated that giving persons with diabetes L-carnitine injections boosted their blood sugar uptake and enhanced their insulin sensitivity. By combining L-carnitine with calorie restriction, a 2010 small study at Sapienza University in Rome discovered that insulin resistance was decreased and insulin sensitivity was elevated.

ALCAR (Acetyl L-Carnitine) Power
Male infertility. When combined with L-carnitine, acetyl-L-carnitine appears to improve sperm motility, which may increase the likelihood of conception in infertile men. Additionally, supplementing with acetyl-L-carnitine and L-carnitine after receiving therapy with NSAIDs appears to increase sperm count and sperm motility in males whose infertility is brought on by enlargement of the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and epididymis. Additionally, taking acetyl-L-carnitine, L-carnitine, L-arginine, and Panax ginseng together appears to boost sperm mobility in males who are infertile because their sperm movement is reduced. In men who are infertile due to swollen prostates brought on by Chlamydia infection, it may also enhance sperm motility and count.
Aging-related problems (memory, tiredness). In older persons with some memory loss, using acetyl-L-carnitine seems to improve memory and mental performance. Taking acetyl-L-carnitine helps older adults feel less physically and mentally exhausted. Additionally, it tends to lessen post-exercise fatigue. Acetyl-L-carnitine and propionyl-L-carnitine taken orally may alleviate symptoms brought on by low levels of male hormones. Similar to how the male hormone testosterone works, this combination, when taken for six months, seems to treat sexual dysfunction, depression, and exhaustion.
Alzheimer’s disease. In certain Alzheimer’s patients, acetyl-L-carnitine may enhance memory, several measures of mental function, and behavior. It may also delay the rate at which the illness progresses. Those with early-onset Alzheimer’s disease who are younger than 66 and have a quicker pace of disease development and mental impairment are more likely to benefit from it.
Alcohol withdrawal. Acetyl-L-carnitine reduces withdrawal symptoms and lengthens the period between drinking alcohol when given intravenously (via IV) for 10 days and then orally for 80 days. However, the first week is when symptoms start to improve the most. Therefore, it is unclear whether oral acetyl-L-carnitine supplementation after IV therapy provides any further benefits.
Side-effects
When taken orally, acetyl-L-carnitine is probably safe for the majority of adults. Side effects including nausea and upset stomach could make bipolar disorder symptoms worse in persons who are presently in remission. Additionally, it might make symptoms worse for certain persons who have taxanes-related nerve discomfort after chemotherapy. It has been suggested that acetyl-L-carnitine may interfere with thyroid hormone. L-carnitine, which is related to acetyl-L-carnitine and has been used by people with a history of seizures, has been associated with an increase in the frequency or intensity of seizures.
8. BCAA (Branched-Chain Amino Acids)
BCAA (Branched-Chain Amino Acids) is actually made up of three essential amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Like other amino acids, they are the protein building blocks, and BCAA makes up about 35% of the muscle protein in your body. The amino acids are essential as your body cannot make them alone and you need to get them from the food you eat.
BCAA also protects glycogen tissue, which is what drives the muscles during exercise and minimizes protein breakdown. Thus, athletes take them to reduce muscle breakdown during intense exercises and prevent tiredness, but also to increase performance, stimulate protein building in muscles, and improve concentration.
Benefits
Enhances muscle growth. One study published found that people who consumed a BCAA after resistance training experienced 22 percent more muscle protein synthesis than a control group.
Speeding up recovery time. Eight studies published in Nutrition concluded that BCAA supplementation is a more effective strategy to speed up recovery than rest following intense exercise.
Promotes liver health. A review of 11 studies found that taking BCAAs could improve liver function in patients undergoing liver surgery, reducing the risk of complications, and the duration of hospital stays.
Prevents muscle loss. BCAA was effective at reducing the breakdown of muscle in the body in humans, for example from the side effect of chronic conditions like cancer or premature aging.
Improves athletic performance. For instance, a study from Leeds Metropolitan University in the U.K. revealed that adding leucine to a resistance training regimen for a period of 12 weeks significantly improved strength performance.
Increases weight loss. In one study, using a branched-chain amino acid supplement increased lean body mass and decreased body fat more effectively than whey protein when combined with resistance training in 36 men.
Other benefits. Some evidence suggests BCAA may be effective for treating other conditions, such as Anorexia, Liver Disease, and Mania.

BCAA (Branched-Chain Amino Acids)
Side-effects
Although BCAA is generally safe, if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, there is inadequate reliable information about the safety of taking branched-chain amino acids. Children may be healthy when taken by mouth for a short period (up to 6 months). When used in patients with ALS, branched-chain amino acids were associated with lung failure and higher death rates.
Dietary use of BCAA is connected to liver disease among alcoholics, which could result in brain damage (hepatic encephalopathy). BCAA can influence blood sugar levels, which may interfere with regulating blood sugar during and after surgery. Fatigue, poor coordination, and stomach issues are other frequent adverse effects.
9. Creatine
Creatine is probably the most popular performance-enhancing drug among athletes is now creatine. It is a substance that all organisms naturally possess and in which adenosine triphosphate (ATP) may be recycled with ease. ATP is the “energy currency” of the cell and is mostly present in muscle and brain tissue. Some of the creatine that the body requires can be produced by it, but it also comes from foods high in protein, such meat and fish.
Creatine is thought to boost power, enhance lean muscle mass, and hasten muscle recovery after exercise. Especially during brief bursts of high-intensity exercise like weightlifting or running, this muscular surge can aid athletes in achieving speed and energy bursts. Benefits increased lean muscle mass growth by assisting with protein synthesis. Weight gain is also a result of water retention. According to several studies, using creatine supplements for one week increased body mass by roughly 0.9–2.2 kilos (2.0–4.6 pounds).
Benefits
Increased lean muscle mass growth by assisting with protein synthesis. Weight gain is also a result of water retention. According to several studies, using creatine supplements for one week increased body mass by roughly 0.9–2.2 kilos (2.0–4.6 pounds).
Improved endurance and power efficiency. Although the muscles’ ability to store creatine is relatively little, it grows as muscle mass does. When engaged in vigorous exercise, supplemental support may help ATP reserves recover more quickly, preserving energy and lowering weariness.
Recuperation of muscles after exercise and the performance after strength training.
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) seems to boost performance. According to studies, work done during sets of complete muscular contractions, single-effort sprint performance, and repeated sprint performance all improved.
Neuroprotective properties, which means it may help to protect the brain.
Improvement in cognition, including increased alertness, awareness, and focus.
May lessen depression symptoms, according to animal studies and limited human pilot trials.
Heart and blood vessel protection due to its cardioprotective characteristics. Anaerobic cardiovascular capacity and increased endurance have also been found to be beneficial.
Alleviating weariness and general fatigue, while the inadequate amount induces feelings of tiredness.
Aids in building up bone density, particularly when used in conjunction with resistance training.
Side-effects
Although, creatine is typically thought of as a healthy supplement, it is not advised for persons with diabetes, renal, or liver illness. Others who should avoid taking it are pregnant or nursing children under the age of 18 and women. Moreover, you need to drink enough water to prevent dehydration if you are taking creatine.
10. AAKG (Arginine Alpha-Ketoglutarate)
L-Arginine Alpha-Ketoglutarate (AAKG) is a nutritional supplement made up of the amino acid arginine and the substance alpha-ketoglutarate, which breaks down carbohydrates and amino acids.
It is formed as a salt from the combination of two parts arginine and one-part alpha-ketoglutarate. AAKG may benefit muscle growth and performance and also produces nitric oxide, a molecule essential to healthy circulation and cell communication. Alpha-ketoglutarate is used for kidney disease, intestinal and stomach disorders, and many other conditions of which there is yet no good scientific evidence. Alpha-ketoglutarate is occasionally administered intravenously by medical professionals to prevent muscle breakdown stress and damage to the heart during heart surgery.
Benefits
Enhancing anaerobic activity. In 2006, two modest double-blind studies yielded encouraging findings for healthy men between the ages of 30 and 50. Researchers discovered that taking AAKG supplements raised arginine levels and positively impacted peak power production on the wingate and bench press tests. These two activities fall under the category of anaerobic exercises, which are short-duration, high-intensity exercises that are popular in non-endurance sports like bodybuilding and sprinting.
Bringing down blood pressure. Because arginine boosts the production of nitric oxide, a signaling chemical your body generates that encourages blood arteries to dilate, some people take AAKG. Patients who suffer from high blood pressure might benefit from this characteristic. Taking arginine temporarily decreased blood pressure in adults with Type 2 diabetes and mild hypertension, according to a small research. The effect, according to the scientists, is brought on by arginine raising blood vessel nitric oxide levels.
Potential cancer-preventive effect. Researchers examined Alpha-Ketoglutarate’s anti-cancer potential in one study in 2012. Previous research had demonstrated that alpha-ketoglutarate inhibited the development of tumors in cells depleted of oxygen (hypoxia). Alpha-ketoglutarate was discovered to effectively stop colon cancer from spreading to cells even with normal oxygen levels, according to research. More research is required because this study was conducted in a lab using grown cancer cells.
Side-effects
In general, AAKG is well tolerated, and there have been no major side effects or anomalies observed. People who are prone to cold sores or genital herpes may need to avoid arginine supplements because the virus needs arginine to replicate. When taken orally for up to three years, AAKG is probably safe for the majority of adults.
11. SAM-e (S-Adenosylmethionine)
SAM-e (SAMe, S-adenosylmethionine) is a naturally occurring compound in the body that plays an important role in regulating key functions of living cells. In the body, SAMe is made from methionine, an essential amino acid such as found in the human body. In egg whites, wild fish, oats and sesame seeds. SAMe was discovered in Italy in 1952, but has been available as a dietary supplement in the United States for 20-30 years. It is also now gaining attention in Europe and Asia.
SAMe plays a role in the development of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) as a fuel source in our cells. It is also involved in an important process called methylation, which contributes to many biochemical reactions that occur in the body. This includes repair of chromosomes, DNA, maintenance of cell membrane fluidity, protein synthesis, neurotransmitters, and lipid and mineral metabolism. SAMe increases serotonin turnover and increases levels of the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine. It has proven anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties and is commonly used to relieve pain while improving physical function. Additionally, SAMe can be used to treat anxiety, hepatitis, arthritis, and fibromyalgia.
Benefits
Antidepressant effects. Numerous placebo-controlled studies have indicated the antidepressant effect of SAMe, but there is still no conclusive evidence. Some researchers have found that SAMe tends to be lower in depressed individuals compared to people without reported signs of depression, so it’s believed that it does have a beneficial effect, but so far trials have only lasted a some weeks on a limited number of people. A meta-study in 2016 showed SAMe is effective in treating major depressive disease. Experimenters also indicated that recent findings demonstrate SAMe’s efficacy in cases that are non-responsive to SSRI and SSNRI (selective serotonin/-norepinephrine reuptake impediments) medications.
Relieving osteoarthritis. The effectiveness of SAMe as a dietary supplement for the treatment of osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease is still being investigated. Animal studies demonstrate that SAMe promotes cartilage growth, which is necessary for reversing the disease process. Because it can raise glutathione levels and its anti-inflammatory qualities, it can also aid in reducing pain and rigidity. SAMe appears to be as efficient as NSAIDs in lowering pain and enhancing functional limitation in people with osteoarthritis, according to a 2002 study. Patients taking NSAIDs for osteoarthritis were likewise less likely to report side effects when taking SAMe.
Improving symptoms of fibromyalgia. Pain in the muscles and connective tissues that is chronic and extensive is fibromyalgia. People who have this syndrome frequently experience chronic pain, exhaustion, sadness, and mood issues. One double-blind research that lasted six weeks provides modest indication that SAMe can reduce some fibromyalgia symptoms. In comparison to placebo-treated patients, those with fibromyalgia who were given 800 mg orally reported greater mood, less pain, weakness, and morning stiffness.
Supporting liver function. According to research, people with chronic liver illness have inhibited SAMe production, which may aggravate liver damage. SAMe can be included in a medicine regimen for liver health and seems to be very effective in aiding in the improvement of liver function. Before specific suggestions can be made, more research into the fundamental therapy of liver illness with SAMe is required.
May improve brain function. SAMe participates in methylation, a crucial procedure that helps the body’s metabolic processes, especially those in the brain, function. Age-related decreases in methylation capacity raise the risk of neurological illnesses like Alzheimer’s. There is evidence that SAMe levels are lower in Alzheimer’s sufferers, which may impair their metabolism and cognitive performance.
In addition, SAMe contributes to the synthesis of glutathione, a potent antioxidant that operates within cells. Reduced glutathione may contribute to Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative illnesses, according to studies. In one animal model meta-analysis, the impact of SAMe on mice’s maze performance—a test of cognitive ability—was assessed. Researchers hypothesized that taking SAMe supplements enhanced cognitive function.
Works as natural pain reliever. The effects of SAMe supplements on pain alleviation have attracted attention because they are used to treat lower back pain, joint discomfort, PMS symptoms, and stomach pain. The analgesic effects of SAMe are still being studied, but there are some encouraging research. A tiny trial from 2013 discovered that oral SAMe, at a median dose of 1,400 milligrams per day for two months, could lessen children’s stomach pain. After receiving SAMe treatment, patients’ reported pain levels improved, according to researchers.
May improve asthma symptoms. SAMe was discovered to have a suppressive effect on airway fibrosis and inflammation in a 2016 animal investigation of mice with persistent asthma. Researchers came to the conclusion that SAMe may have promise as a novel therapeutic agent for those with chronic asthma symptoms, but human trials are required to determine whether it may effectively lower oxidative stress and reduce airway inflammation.
Side-effects
The medication SAMe appears to be comparatively safe. High doses of oral SAMe may result in symptoms like skin rashes, anxiety, headache, dry mouth, constipation, gas, diarrhea, and insomnia. For those who suffer from illnesses like diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, or bipolar disorder, SAMe might not be safe. Stop using SAMe two weeks before surgery since it may widen the blood vessels. Safety of SAMe use during pregnancy or breast-feeding is not known.
12. L-Glutamine
Glutamine is an amino acid found naturally in humans. D-glutamine appears to be rather unimportant in live creatures, but L-glutamine is necessary for the synthesis of proteins as well as other processes. It is also an important molecule for the immune system and intestinal health.
L-glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the blood and other body fluids. However, there are times when the glutamine needs of your body are greater than its ability to produce it. Therefore, it’s considered a conditionally essential amino acid, meaning that it must be obtained from the diet under certain conditions, such as injury or illness.
Benefits
Healthy gut function. L-glutamine might help gut function, the immune system, and other essential processes in the body, especially in times of stress. It is crucial for giving many different types of cells their nitrogen and carbon. The body needs glutamine to produce other substances like other amino acids and glucose (sugar).
Recovery from surgery. L-glutamine is given to help people recover from surgery, injuries, burns, bone marrow transplant. Nitrogen is essential for wound healing and maintaining the function of the important organs following surgery or acute injury. This nitrogen is made up of around one-third glutamine.
Replenish levels during HIV/AIDS. If the body uses more glutamine than the muscles can make (i.e., during times of stress), muscle wasting can occur. Those who have HIV/AIDS are susceptible to this, in which case taking supplements with glutamine could maintain adequate glutamine levels.
Replenish levels during chemotherapy. Some types of chemotherapy can reduce the levels of glutamine in the body. By extending the life of the damaged tissues, glutamine therapy is supposed to aid in preventing chemotherapy-related harm.
Side-effects
When taken orally in amounts up to 40 grams per day, glutamine is probably safe for the majority of individuals. Generally minor side effects, such as nausea, heartburn, and stomach pain, can occur. However, persons who are sensitive to MSG should stay away from L-glutamine as it can exacerbate cirrhosis, mania, and hepatic encephalopathy.
13. NMN (β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN, β-NMN) is a nucleotide composed of vitamin B3 (nicotinamide), a sugar molecule (ribose), and a phosphate molecule. Like nicotinamide riboside, NMN is a derivative of niacin, and humans have enzymes that can use NMN to generate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). In mice, NMN enters cells via the small intestines within 10 minutes converting to NAD+ through the Slc12a8 NMN transporter.
NAD+ levels decline with age, and this decline is thought to be associated with accelerated physical decline and the onset of age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s. Animal studies have shown that supplementing with NAD+ precursors NMN and NR restores NAD+ levels and prevents age-related physical decline. NAD+ is a compound found in every cell in your body and involved in many critical processes, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression. NMN supplementation in turn has prevented age-associated genetic changes and improved energy metabolism, physical activity, and insulin sensitivity.
Because NADH is a cofactor for processes inside mitochondria, for sirtuins, and for PARP, NMN has been studied in animal models as a potential neuroprotective and anti-aging agent.
NMN can be given safely to mice and is found naturally in a number of foods, including broccoli, cabbage, cucumber, edamame and avocado. The new study shows that when NMN is dissolved in drinking water and given to mice, it appears in the bloodstream in less than three minutes. Importantly, the researchers also found that NMN in the blood is quickly converted to NAD in multiple tissues.
In skeletal muscle NMN administration helps energy metabolism by improving the function of mitochondria, which operate as cellular power plants. They also found that mice given NMN gained less weight with aging even as they consumed more food, likely because their boosted metabolism generated more energy for physical activity.
Benefits
Beneficial Effects on Aging. NMN is quickly absorbed and converted to NAD when administered orally, which several studies have shown increases NAD levels, decreases inflammation in aging adipose tissue, increases insulin secretion and action, enhances mitochondrial function, enhances brain neuronal function, and more.
Longer Lifespan. There are several studies that show lifespan is extended in mice, while longer studies on humans are ongoing.
Enhances Muscle Growth. One study published found that people who consumed a NMN after resistance training experienced 22 percent more muscle protein synthesis than a control group. NMN was also effective at reducing the breakdown of muscle in the body in humans, for example from side effect of chronic conditions like cancer or normal part of the aging process. Recent research on amateur runners showed that an increased exercise-induced human aerobic capacity when using NMN.
Reducing Frequency of Metabolic Diseases. Animal research have revealed promising findings concerning the function of NAD boosters in reversing the effects of high-fat diets, reducing body weight, and enhancing energy levels. According to the findings of a small clinical study, women with prediabetes who took NMN for 10 weeks had better muscle glucose metabolism.
Natural NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide)
More Energy and Stamina. Although there isn’t much clinical proof for this advantage, studies on mice reveal that NMN can boost stamina and endurance by up to 80%.
Enhanced Cognitive Performance. Studies on rodents back up the idea that NMN enhances a number of crucial mental processes, including cognition and memory in models of Alzheimer’s disease.
Side-effects
There are no documented negative effects of NMN. Numerous studies have demonstrated that even at extremely large doses of NMN administered to mice there are no harmful or adverse consequences. According to human clinical toxicity study at Keio University in Japan, NMN can be supplied safely and is efficiently digested in the body.
14. NR (Nicotinamide Riboside)
Nicotinamide riboside (NR, NR-Cl) is a slightly smaller molecule to NMN, as it composed only of vitamin B3 (nicotinamide or niacin) and a sugar molecule (ribose). This vitamin B3 substance is known by the name niagen.
The body transforms nicotinamide riboside into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), a coenzyme or helper molecule, much like it does with other forms of vitamin B3. Many important biological activities, including the following, use NAD as fuel:
- Repairing damaged DNA
- Enhancing cell defense mechanisms
- transforming food into energy
- regulating the circadian rhythm
However, as you age, your body’s natural level of NAD declines. At this time, chronic diseases occur with lowered NAD levels, such as diabetes, heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and eyesight loss. Interestingly, animal studies have discovered that increasing NAD levels may help prevent many chronic diseases and reverse indications of aging.
Natural sources of NR are cow’s milk, yeast, and beer, but they only contain trace levels of niacin. Nicotinamide riboside supplements have swiftly gained popularity, as they seem to be particularly successful at increasing NAD levels.
Benefits
Nicotinamide riboside increases blood NAD levels by up to 2.7 times, according to animal studies. Additionally, compared to other NAD precursors, it is utilised by your body more quickly.
NAD reacts by activating enzymes that repair DNA damage and in aid healthy aging. Sirtuins are one such family that seems to extend the life span of animals and enhance general health. Studies show that sirtuins may restore DNA damage, increase stress resistance, lessen inflammation, and provide other advantages that support healthy aging. (Notably, the advantages of calorie restriction for increasing lifespan are also due to sirtuins.)
Another category of enzymes that restores DNA damage are Poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerases (PARPs). Higher PARP activity has been linked in studies to reduced DNA damage and a longer life span.
May help protecting the brain and neurons. Researchers think that age-related brain illnesses including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease are associated with both oxidative stress and decreased mitochondrial activity.
NAD aids in the regulation of PGC-1-alpha synthesis in brain cells, a protein that appears to help shield cells against oxidative stress and compromised mitochondrial function. NR increased brain NAD+ levels and PGC-1-alpha synthesis in Alzheimer’s disease-affected mice by up to 70% and 50%, respectively. By the end of the experiment, the mice significantly outperformed the humans in memory-based activities.
In a study using stem cells from a Parkinson’s patient, nicotinamide riboside increased NAD+ levels and markedly enhanced mitochondrial performance.
May reduce the risk for heart disease risk. Coronary disease is the largest cause of death worldwide and heavily influenced by aging. Your aorta, for example, may become thicker, stiffer, and less flexible as a result. These alterations can increase blood pressure and put more strain on your heart.
NR increased NAD levels in humans, assisted in reducing aortic stiffness, and decreased systolic blood pressure in people at risk of high blood pressure. NR have also helped mice increase their metabolism, which may help with weight loss.
Potentially lowering the risk of cancer. High NAD levels aid in the prevention of oxidative stress and DNA damage, which are connected to the development of cancer.
Side-effects
The observed side-effects of NR are small. Studies on humans find that taking 1-2 gram daily has no harmful effects. Mild to moderate side effects for some people, include as headaches, fatigue, diarrhea, and nausea.
15. Resveratrol
Resveratrol is often cited as a one explanation for the French Paradox, which refers to the surprisingly low prevalence of coronary heart disease in France. Resveratrol, which is found in the skin and seeds of red wine grapes, is a key to the conundrum.
Resveratrol is a polyphenol that is produced especially within stressed plants. It is a defense mechanism produced by plants to ward off fungi, defend themselves from dehydration, or shield themselves from harmful UV radiation. This type stress response phenomena in organisms has been called hormesis.
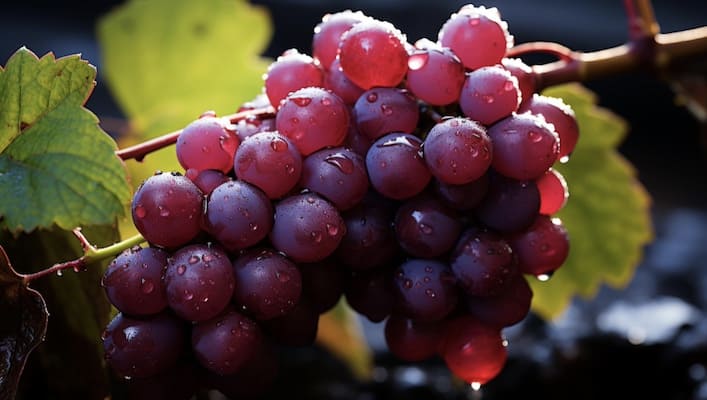

Resveratrol is found in small amounts in the skin of red grapes
Benefits
The benefits of resveratrol are numerous and astounding and includes it being anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective. It has been used to treat blood pressure, stomachaches, hepatitis, arthritis, urinary tract infections, fungal disorders, and skin irritation, according to one peer-reviewed article.
Numerous studies indicate that resveratrol has a wide range of physiological effects on people. The strong antioxidant properties comes from the capacity to function as both a direct antioxidant and as what researchers refer to as an indirect cellular antioxidant system inducer is largely responsible for the amazing potential that numerous studies have shown in this area. In other words, it is actively scavenging free radicals and defending cells from oxidative stress on several levels. Reduced blood pressure and a decreased risk of age-related cognitive decline are positive side effects of resveratrol antioxidant qualities, while additional research is need to draw firm conclusions.
Resveratrol may also be a useful substance for the management and prevention of a number of cancer types, e.g. breast cancer. It functions at each of the three stages of carcinogenesis, or the process by which healthy cells develop cancer, by altering the pathways that regulate cell division and proliferation. Additionally, it may interfere with the expression of some hormones, which could prevent the spread of hormone-dependent tumors, and it can affect the gene expression in cancer cells, which slows down the growth of these cells. Although further clinical trials are required, what is known thus far is quite intriguing.
Resveratrol may have cardioprotective benefits. It uniquely seem to be beneficial for several conditions connected to cardiovascular disease and heart failure.
Perhaps the most important effect is the potential of resveratrol to activate sirtuins, a family of seven protein enzymes intimately linked to cellular health regulation and lifespan in animals. Resveratrol specifically activates the SIRT-1 sirtuin, a mechanism that has an antioxidant effect, increased insulin resistance, and support for the musculoskeletal and neurological systems. Resveratrol is a key component of the it is a powerful polyphenol that has likely undergone the most investigation of all the known sirtuin enhancers.
Side-effects
Resveratrol does not have considerable side-effects at typical doses (1-2 gram). However, it does have a moderate blood thinning effect, may lower blood pressure, and can slow blood clotting. Because of these effects you should speak with your doctor if you are taking blood thinning medications or if you are scheduled for a surgery.
16. Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid found in many fruits and vegetables, including onions, apples, and berries. It has gained attention in recent years for its potential health benefits, including its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Quercetin is a flavonoid with several potential health benefits, including its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, potential to support cardiovascular health and immune system function, and potential to inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Benefits
Antioxidant. Quercetin has been found to have antioxidant properties, which can help to protect the body against damage from free radicals. Free radicals can contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Anti-inflammatory. Quercetin has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is a common factor in the development of many diseases.
Cardiovascular health. Quercetin has been found to have cardioprotective properties and may help to reduce the risk of heart disease. It has been studied as a potential treatment for high blood pressure and atherosclerosis.
Immune function. Quercetin has been found to have immunomodulatory properties and may help to support immune system function. It has been studied as a potential treatment for allergies and other immune system disorders.
Anticancer. Quercetin has been found to have potential anticancer properties, which can help to inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells. It has been studied as a potential treatment for various types of cancer, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer.
Side-effects
Quercetin has limited bioavailability, meaning that the body may not absorb it well. This can make it difficult to achieve therapeutic levels of quercetin through dietary sources alone.
Some people may experience side effects from quercetin supplements, including digestive upset, headaches, and allergic reactions. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider before using quercetin if you have any health conditions or are taking any medications.
Quercetin may interact with some medications, including blood thinners and medications for anxiety and depression. If you are taking any medications, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider before using quercetin.
Quercetin supplements are not recommended for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to a lack of safety data.
17. Rhodiola Rosea Root
Rhodiola rosea root is an herb that has been traditionally used for centuries in countries such as Russia, Scandinavia, and China for its purported health benefits. It is often marketed as an adaptogen, which is a natural substance that helps the body adapt to stress and maintain homeostasis. In recent years, rhodiola rosea has gained popularity as a dietary supplement, with claims that it can improve physical and mental performance, reduce fatigue, alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, and provide neuroprotection.
Benefits
Improves physical performance. Some studies suggest that rhodiola rosea may improve endurance and reduce fatigue, making it an attractive supplement for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. In a 2010 study, for example, a group of male students taking rhodiola rosea supplements for four weeks experienced an increase in time to exhaustion during exercise.
Enhances mental performance. Rhodiola rosea has also been shown to have cognitive-enhancing effects. A 2015 study found that rhodiola rosea supplements improved mental fatigue and concentration in physicians working night shifts.
Reduces stress and anxiety. Rhodiola rosea may also have anxiolytic properties, helping to reduce symptoms of stress and anxiety. A 2017 systematic review of 11 clinical trials found that rhodiola rosea had significant anti-stress effects.
May have neuroprotective properties. Rhodiola rosea has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which may help protect the brain from age-related decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Side-effects
While rhodiola rosea is generally considered safe, some users have reported adverse effects such as dizziness, dry mouth, and gastrointestinal discomfort. High doses may also cause irritability, insomnia, and restlessness.
Rhodiola rosea may interact with certain medications, including antidepressants, blood thinners, and diabetes medications. People taking these medications should consult with their healthcare provider before taking rhodiola rosea.
Despite the promising results of some studies, the overall research on rhodiola rosea is still limited. More research is needed to confirm its effectiveness for various health conditions, as well as to determine the optimal dosage and long-term safety.
Not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding: Rhodiola rosea should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding, as there is limited research on its safety during these periods.
18. Maca Root
Maca root extract is derived from the root of the maca plant, which is native to the high Andes mountains of Peru. It has been used for centuries as a traditional medicine and food source, and is often marketed as a dietary supplement for its purported health benefits. Maca root is a popular dietary supplement that may offer a range of potential benefits, including improved sexual function, enhanced energy and endurance, mood enhancement, and menopausal symptom relief.
Benefits
Improved sexual function. One of the most commonly touted benefits of maca root extract is its potential to improve sexual function, including libido and erectile dysfunction. A 2010 study found that men taking maca root extract for 12 weeks reported an improvement in sexual desire compared to those taking a placebo.
Enhanced energy and endurance. Maca root extract is often marketed as an adaptogen, which means it may help the body adapt to stress and fatigue. Some studies suggest that it may improve energy and endurance, making it an attractive supplement for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
Mood enhancement. Maca root extract has been shown to have positive effects on mood, reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression in some studies. A 2018 systematic review of eight studies found that maca root extract had significant antidepressant effects.
Menopausal symptom relief. Maca root extract may also be beneficial for women experiencing menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness. A 2016 systematic review of nine studies found that maca root extract had a significant effect on reducing menopausal symptoms.

Maca root powder
Side-effects
While maca root extract is generally considered safe, some users have reported adverse effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, and insomnia. High doses may also cause irritability and anxiety.
Maca root extract may interact with certain medications, including those used for diabetes and high blood pressure. People taking these medications should consult with their healthcare provider before taking maca root extract.
Maca root extract contains compounds that may affect hormone levels in the body, particularly in women. While some studies suggest it may have a positive effect on hormone balance, more research is needed to fully understand its hormonal effects.
19. Mucuna Pruriens
Mucuna Pruriens, also known as velvet bean, is a legume native to Africa and tropical Asia. The extract is a popular dietary supplement that may offer a range of potential benefits, including improved mood and motivation, reduced symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, increased testosterone levels, and improved fertility.
Benefits
Improved mood and motivation. Mucuna Pruriens extract has been shown to improve mood and motivation in several studies. This may be due to its ability to increase dopamine levels in the brain, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in regulating mood and motivation.
Reduced symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The L-DOPA content in Mucuna Pruriens extract makes it a potential treatment for Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a lack of dopamine production. Studies have found that Mucuna Pruriens extract may be as effective as traditional Parkinson’s medications, with fewer side effects.
Increased testosterone levels. Mucuna Pruriens extract has also been shown to increase testosterone levels in men. This may lead to improved muscle mass, strength, and athletic performance.
Improved fertility. Mucuna Pruriens extract has been used in traditional medicine for its potential to improve fertility. Some studies have found that it can improve sperm quality and increase the chances of conception in both men and women.
Side-effects
Mucuna Pruriens extract is generally considered safe, but some users may experience adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, but it is still important to be aware of them.
Mucuna Pruriens extract may interact with certain medications, including those used for Parkinson’s disease and depression. It may also interfere with the absorption of certain nutrients, such as iron and vitamin B6.
While short-term studies have found Mucuna Pruriens extract to be generally safe, there is limited research on its long-term safety. More studies are needed to determine any potential risks associated with long-term use.
The quality and purity of Mucuna Pruriens extract supplements can vary greatly. Some products may be contaminated with heavy metals or other harmful substances, while others may not contain the advertised amount of L-DOPA. It is important to purchase supplements from a reputable source and to ensure that they have been third-party tested for quality and purity.
20. Tribulus Terrestris
Tribulus terrestris is a plant that is commonly used in traditional medicine to treat a range of conditions. It is particularly well-known for its potential benefits in boosting testosterone levels, which has led to its use as a sports supplement and for higher athletic performance.
Benefits
Increased male hormone. One of the main reasons why people use terrestris is its potential ability to increase testosterone levels. Some research has found that it may be effective in increasing testosterone levels in men, which can lead to improved muscle mass, strength, and performance.
One study found that men who took Tribulus terrestris supplements for 90 days had a significant increase in testosterone levels compared to a placebo group. Other studies have reported similar findings, with some suggesting that Tribulus terrestris may be effective in improving libido and sexual function in both men and women.
Libido among men and women. Tribulus may also have a positive effect on sexual function by improving libido and sexual satisfaction. In a study of 180 men with erectile dysfunction, those who took a Tribulus terrestris extract for 60 days showed a significant improvement in sexual function, including increases in libido and erectile function.
Similarly, in a study of 50 women with sexual dysfunction, those who took a Tribulus terrestris extract for 90 days reported significant improvements in desire, arousal, and satisfaction. Other studies have reported similar findings, with some suggesting that Tribulus terrestris may be effective in improving libido and sexual function in both men and women. It is thought that Tribulus terrestris may have a positive effect on libido and sexual function by increasing levels of testosterone, which is a hormone that plays a key role in sexual desire and function.
Cardiovascular health. Some studies have suggested that terrestris may have anti-inflammatory properties, which could potentially benefit cardiovascular health. One study found that a Tribulus terrestris extract was able to reduce inflammation in rats with induced myocardial infarction. Additionally, a study on human subjects with high cholesterol levels found that taking a Tribulus terrestris extract for three months led to improvements in markers of cardiovascular health.
Liver Health. Tribulus terrestris has traditionally been used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat liver disease. Some animal studies have suggested that tribulus may have hepatoprotective effects, meaning that it may help to protect the liver from damage. However, it is important to note that high doses of Tribulus terrestris have been associated with liver damage in some studies.
High Blood Pressure. Some research has suggested that terrestris may have a positive effect on blood pressure. One study found that taking a Tribulus terrestris extract for six weeks led to a significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in patients with hypertension.
Headaches. While there is limited research on the use of Tribulus terrestris for headaches, one study found that a Tribulus terrestris extract was able to reduce the frequency and severity of tension headaches in female patients.
Side-effects
One of the main concerns with tribulus terrestris is its potential impact on the liver. Some research has found that high doses of Tribulus terrestris may cause liver damage, which could lead to liver disease or other serious health problems. Therefore, it is important to use Tribulus terrestris with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Another potential concern with tribulus is its impact on hormone levels. While it is often used as a testosterone booster, some research has suggested that it may also have an estrogenic effect, potentially leading to an imbalance in hormone levels. This could be particularly concerning for men, who may experience a range of symptoms as a result of high estrogen levels.
Finally, some people may experience side effects when using Tribulus terrestris, such as gastrointestinal upset, headaches, and sleep disturbances. Additionally, because it is often used as a sports supplement, there is a risk that some people may misuse or abuse it.
21. Fenugreek Seed
Both Fenugreek seed extract and fenugreek ground powder derived from the seeds of the fenugreek plant, which is native to the Middle East and India. It has been used for centuries as a spice and traditional medicine, and in recent years, fenugreek seed extract has gained popularity as a natural remedy for a variety of health issues, including improved blood sugar control, increased milk production in breastfeeding mothers, reduced inflammation, improved digestive health, and increased testosterone levels.
Benefits
Improved blood sugar control. Fenugreek seed has been found to be effective in improving blood sugar control in people with type 2 diabetes. It works by slowing down the absorption of carbohydrates in the intestines and increasing insulin sensitivity, which helps to reduce blood sugar levels.
Increased milk production in breastfeeding mothers. Fenugreek has been traditionally used to increase milk production in breastfeeding mothers. Studies have found that it can increase milk production by up to 900%, likely due to its ability to stimulate the production of the hormone prolactin.

Fenugreek seed
Reduced inflammation. Fenugreek seed has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the body. This may help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and arthritis.
Improved digestive health. Fenugreek seed extract has been found to help improve digestive health by reducing constipation, improving gut motility, and reducing symptoms of acid reflux and heartburn.
Increased testosterone levels. Fenugreek may help to increase testosterone levels in men, which can lead to improved muscle mass, libido, and energy levels.
Side-effects
Fenugreek can cause gastrointestinal side effects in some people, including gas, bloating, and diarrhea. These side effects are generally mild and can be reduced by taking the supplement with food.
Some people may have an allergic reaction to fenugreek seed extract, which can cause symptoms such as itching, hives, and difficulty breathing.
Fenugreek can interfere with the effectiveness of some medications, particularly blood-thinning medications and medications for diabetes. If you are taking any medications, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider before taking fenugreek seed extract.
While fenugreek can be effective in improving blood sugar control in people with diabetes, it can also lower blood sugar levels too much in some people. This can cause symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and fainting.
In rare cases, fenugreek seed extract can cause a maple syrup-like odor in sweat and urine. This is due to the presence of a compound called sotolon, which is found in maple syrup and fenugreek seeds.
22. Butea Superba
Butea superba is a plant native to Thailand and other parts of Southeast Asia, and it has been used in traditional medicine for a variety of purposes. Recently, it has gained attention as a potential natural remedy for sexual dysfunction, particularly in men. Here is a summary of the potential benefits and drawbacks of using Butea superba.
Benefits
Sexual Function. The most commonly cited benefit of butea is its potential to improve sexual function in men. Several studies have reported that the herb may increase sexual desire, improve erectile function, and boost overall sexual satisfaction. One study found that men who took Butea superba for three months experienced significant improvements in sexual function compared to those who received a placebo.
Antioxidant. Butea superba contains high levels of antioxidants, which can help protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. One study found that an extract of the herb had a strong antioxidant effect, helping to reduce oxidative stress in the body.
Anti-Inflammatory. Butea has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. In one study, researchers found that an extract of the herb was able to reduce inflammation in rats with arthritis. This suggests that the herb may have potential as a natural remedy for inflammatory conditions in humans.
Aphrodisiac. Butea superba has traditionally been used as an aphrodisiac in Thailand, and some studies suggest that it may have potential in this area. In one study, researchers found that the herb was able to increase the number of sexual behaviors and the duration of copulation in male rats. This suggests that Butea superba may have potential as a natural aphrodisiac in humans as well.
Blood Sugar Control. Some preliminary studies suggest that Butea superba may have potential for blood sugar control. In one study, researchers found that an extract of the herb was able to reduce blood sugar levels in rats with diabetes. More research is needed to determine if the herb may have similar effects in humans.
Side-effects
While there is some research to suggest that Butea superba may have potential benefits, the amount of research in this area is still limited. More studies are needed to fully understand the effects of the herb on sexual function, inflammation, and other areas of health.
Some users of Butea superba may experience side effects, such as headache, dizziness, or upset stomach. Additionally, the herb may interact with certain medications, so it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before using it.
Preliminary research suggests that Butea superba may have hormonal effects, particularly on testosterone levels. While this could be beneficial for some men with low testosterone, it could also be harmful in others.
Some people may be allergic to Butea superba, and could experience allergic reactions such as hives or difficulty breathing.
23. Eucommia Bark
Eucommia bark extract is a supplement derived from the bark of the Eucommia ulmoides tree, which is native to China. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries to treat a variety of health conditions. The extract is rich in phytochemicals, including lignans and iridoids, which have been associated with various health benefits. In this summary, we will explore the potential benefits and drawbacks of using Eucommia bark extract.
In conclusion, Eucommia bark extract has the potential to provide a range of health benefits, including joint health, blood pressure management, immune function, sleep quality, sexual function, and anti-aging properties. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and drawbacks of using this supplement. Individuals should consult with their healthcare provider before taking Eucommia bark extract and should purchase supplements from reputable sources to ensure purity and potency.
Benefits
Supports Joint Health. Eucommia bark extract has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties, making it a potential treatment for joint pain and inflammation. One study found that Eucommia bark extract helped to alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis, a common condition that causes joint pain and stiffness.
Blood Pressure Management. Eucommia bark has been shown to have blood pressure-lowering effects, making it a potential treatment for hypertension. One study found that taking Eucommia bark extract for eight weeks helped to lower both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in individuals with high blood pressure.
Boosts Immune Function. Eucommia has been found to have immune-boosting properties. Studies have shown that it can stimulate the production of white blood cells, which help to fight infections and other diseases.
Promotes Healthy Sleep. Eucommia has been found to have sedative properties, making it a potential treatment for insomnia. One study found that taking Eucommia bark extract before bed helped to improve sleep quality in individuals with insomnia.
Enhances Sexual Function. Eucommia extract has been traditionally used as an aphrodisiac in traditional Chinese medicine. Studies have shown that it can increase levels of testosterone and improve sexual function in both men and women.
Anti-Aging Properties. Eucommia bark extract is rich in antioxidants, which can help to protect the body against oxidative stress and the effects of aging. One study found that taking Eucommia bark extract for eight weeks helped to reduce levels of oxidative stress in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
Side-effects
While there is some research supporting the potential health benefits of Eucommia, the majority of studies have been conducted in animals or small human trials. More research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and drawbacks of using this supplement.
Eucommia bark extract is generally considered safe when taken in recommended doses. However, some individuals may experience side effects, such as dizziness, nausea, or upset stomach.

Eucommia ulmoides bark from Chinese Gutta-Percha tree
Eucommia interact with certain medications, including blood pressure medications, anti-inflammatory drugs, and diabetes medications. Individuals taking these medications should consult with their healthcare provider before taking Eucommia bark extract.
Like many dietary supplements, the quality and purity of Eucommia supplements may vary. It is important to purchase supplements from reputable sources and to look for products that have been independently tested for purity and potency.
Eucommia bark extract supplements may be more expensive than other dietary supplements. This may be a drawback for some individuals who are on a tight budget or who are looking for more affordable supplement options.
24. Phosphatidylserine (PS)
Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid, a fatty molecule made by the body that aids in message transmission between brain nerve cells. It facilitates blood coagulation, coats and protects brain cells, and may be essential for maintaining memory acuity.
Some foods naturally contain phosphatidylserine, and it is also offered as a dietary supplement. Levels appear to drop with aging, according to animal studies, but supplementation may help.
Benefits
Phosphatidylserine might be beneficial for problems such as depression, Alzheimer’s disease, Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD / ADHD), difficulties falling asleep, athletic performance, stress and anxiety, and Multiple Sclerosis.
May improve athletic performance Supplements containing phosphatidylserine may help athletes perform better and increase their capacity for exercise. It has been shown that PS may aid reduce muscular soreness and guard against an increase in cortisol levels, a stress hormone that is frequently brought on by overtraining.
Could reduce memory loss. Phosphatidylserine is perhaps the most common dietary supplement used for memory loss in aging people. In one double-blind study, seniors with mild cognitive impairment were given phosphatidylserine supplements or a placebo for six months. Tests conducted after the trial showed a significant improvement in memory in the group taking phosphatidylserine.
Could reduce depression. It appears that phosphatidylserine contributes to positive moods. A 2015 study on participants with serious depression over 65 years old, tested the efficacy taking supplements containing phosphatidylserine and the omega-3 fatty acids (DHA, EPA) three times a day for 12 weeks. There scores on a depression scale showed significant improvement at the end of the trial.
Treatment for ADHD symptoms. A 2012 study published in the journal European Psychiatry raises the possibility that treating children with ADHD symptoms with phosphatidylserine and omega-3 fatty acids. In the study, children were given either a placebo or a phosphatidylserine and omega-3 fatty acid supplement to take for 15 weeks. According to the findings, subjects who received the phosphatidylserine and omega-3 fatty acid combination saw a considerable decrease in hyperactivity and improved impulse control, along with an improvement in mood.
In a another double blind trial in 2014 on children diagnosed with ADHD, treatment with phosphatidylserine during two months significantly improved auditory memory, attention, and impulse control.
Could reduce cortisol levels. A recent study found that phosphatidylserine supplementation lowers the body’s production of the stress-related hormone cortisol. Keeping cortisol levels under control is advantageous because high levels are linked to harmful health impacts like elevated blood glucose and blood pressure.
Side-effects
Phosphatidylserine does have some blood thinning effects. Because of this you may need to check with your health care provider if you are using e.g. blood-thinning-, blood-clotting medications, or are waiting for an operation.
25. Ursolic acid
Ursolic acid is a natural compound found in a variety of plants, including apple peels, rosemary, and holy basil. It has been researched for its potential benefits on health, fitness, muscle building, fat loss, and longevity. In particular, it possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, and anti-aging effects.
Benefits
Anti-obesity effects. Ursolic acid may help with weight loss and prevent obesity. It has been shown to decrease adipogenesis, the process by which new fat cells are formed, and increase lipolysis, the breakdown of fat cells.
One study published in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism found that supplementing with ursolic acid for 12 weeks reduced body fat and improved markers of metabolic health in overweight and obese individuals. The researchers suggested that these effects may be due to the ability to increase energy expenditure and promote the browning of white fat.
Anti-diabetic effects. Ursolic acid can improve glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, making it a promising natural compound for managing type 2 diabetes.
Fitness and exercise performance. One study published in the journal Metabolism found that supplementing with ursolic acid for eight weeks increased muscle mass and strength in healthy men. The researchers attributed these effects to the ability of ursolic acid to enhance insulin signaling and reduce muscle wasting. Another study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food showed that ursolic acid supplementation in mice improved exercise endurance and increased levels of proteins associated with muscle growth.
Other research has investigated the potential benefits of ursolic acid for exercise performance. One study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology showed that supplementation with ursolic acid improved exercise performance and reduced muscle damage in mice. The researchers suggested that these effects may be due to the acid’s ability to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
Anti-inflammatory effects. Ursolic acid has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties. It can reduce the production of inflammatory cytokines and alleviate inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with numerous diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Antioxidant effects. Ursolic acid has potent antioxidant properties, which can help protect the body from oxidative stress. It scavenges free radicals and prevents cellular damage caused by them.

Rosemary contains small amounts of ursolic acid
Anti-cancer effects. Studies have suggested that Ursolic acid may possess anti-cancer properties. It can inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis, a process by which the body eliminates damaged or cancerous cells.
Anti-aging effects. Ursolic acid has been shown to increase the lifespan of fruit flies and mice. It can also protect against age-related decline in cognitive function and muscle mass.
Side-effects
While Ursolic acid has been studied for its potential benefits, there is still limited research on its safety and efficacy in humans. More research is needed to determine its long-term effects and optimal dosage.
Some people may experience side effects when taking Ursolic acid, including digestive issues, headache, and dizziness. However, these side effects are generally mild and rare.
Ursolic acid may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, diabetes medications, and cholesterol-lowering drugs. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking Ursolic acid if you are on any medications.
Ursolic acid is not widely available as a supplement and it can be expensive.
26. L-Ornithine
L-ornithine is a non-protein amino acid that is synthesized in the body through the breakdown of arginine. It is also found in foods such as meat, fish, and dairy products. L-ornithine supplements are commonly used for a variety of purposes, including improved athletic performance, liver detoxification, sleep quality, wound healing, and immune system function.
Benefits
Athletic Performance. L-ornithine supplementation has been found to improve athletic performance in several studies. One study found that taking L-ornithine supplements improved muscle endurance and reduced muscle fatigue during high-intensity exercise. Another study found that L-ornithine supplementation improved power output and reduced the levels of the stress hormone cortisol in athletes.
Liver Health. L-ornithine has been found to have liver-protective effects in several animal studies. It is believed to work by stimulating the production of urea, which helps to remove toxic ammonia from the body. One study found that L-ornithine supplementation reduced liver damage in rats with alcohol-induced liver injury.
Sleep Quality. L-ornithine supplementation has been found to improve sleep quality and reduce fatigue in several studies. One study found that taking L-ornithine supplements improved sleep quality and reduced the time it took for participants to fall asleep. Another study found that L-ornithine supplementation reduced fatigue and improved mood in healthy adults.
Wound Healing. L-ornithine has been found to have wound-healing properties in several animal studies. It is believed to work by stimulating the production of collagen, a protein that is essential for wound healing. One study found that L-ornithine supplementation improved the healing of skin wounds in rats.
Immune System. L-ornithine has been found to have immunomodulatory effects in several studies. It is believed to work by stimulating the production of cytokines, which are molecules that help to regulate the immune system. One study found that L-ornithine supplementation increased the production of cytokines in healthy volunteers.
Side-effects
Ornithine supplementation may cause gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, nausea, and stomach pain. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, but some people may experience more severe symptoms.
Ornithine may interact with certain medications, including antipsychotic drugs, antiepileptic drugs, and drugs used to treat Parkinson’s disease. People taking these medications should consult their healthcare provider before taking L-ornithine supplements.
There is limited information available about the safety of long-term L-ornithine supplementation. Some animal studies have suggested that high doses of ornithine may be toxic to the liver and kidneys.
While L-ornithine supplementation has been found to have several potential benefits, more research is needed to confirm these findings. Many of the studies conducted on ornithine have been small and of short duration, and more rigorous studies are needed to determine the long-term safety and efficacy of L-ornithine supplementation.
27. Cordyceps Sinensis
Cordyceps Mushroom is a type of medicinal mushroom that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. It is grown in the high-altitude regions of China, Nepal, and Tibet and is often consumed in the form of a supplement or tea.
Overall, Cordyceps Mushroom appears to have many potential health benefits, including improved exercise performance, anti-aging effects, immune system support, anti-inflammatory effects, and improved respiratory function.
Benefits
Improved exercise performance. Cordyceps Mushroom has been found to improve exercise performance by increasing oxygen uptake and reducing fatigue. It has also been found to enhance athletic performance and increase endurance in athletes.
Anti-aging effects. Cordyceps Mushroom contains antioxidants, which can help to protect the body against damage from free radicals. This can help to reduce the signs of aging and promote overall health and longevity.
Immune system support. Cordyceps Mushroom has been found to have immune system-boosting effects. It can help to increase the production of white blood cells and enhance the activity of natural killer cells, which are important for fighting off infections.
Anti-inflammatory effects. Cordyceps Mushroom has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects, which can help to reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to many chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Improved respiratory function. Cordyceps Mushroom has been found to have respiratory-supporting effects. It can help to improve lung function and reduce symptoms of respiratory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Side-effects
While Cordyceps Mushroom is generally considered safe, there are some safety concerns. For example, it may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and immunosuppressants.
Cordyceps Mushroom can be expensive, particularly if you opt for a high-quality product. This can be a barrier for some people who are interested in trying it but cannot afford it.
While there is some evidence to support the potential health benefits of Cordyceps Mushroom, the research is still limited. Many of the studies have been done in animals or test tubes, and more research is needed to determine if these effects translate to humans.
28. Tongkat Ali
Tongkat ali, also known as Eurycoma longifolia, is a medicinal herb native to Southeast Asia that has been used for centuries to improve energy, mood, and sexual function.
Benefits
Boosts athletic performance. Tongkat ali has been shown to increase muscle mass, strength, and endurance, making it a popular supplement among athletes and bodybuilders. It works by increasing testosterone levels and reducing cortisol, a stress hormone that can inhibit muscle growth.

Cordyceps militaris mushrooms
Increases energy. Tongkat ali has been shown to increase energy levels, reduce fatigue, and improve mental clarity. It works by increasing levels of ATP, the body’s primary energy source.
Enhances libido. One of the most well-known benefits of tongkat is its ability to improve sexual function in both men and women. This is due to its ability to increase testosterone levels, which leads to improved libido, sperm quality, and erectile function.
Improves mood. Tongkat ali has been shown to have an anti-anxiety effect, which can improve mood and reduce stress levels. It works by increasing levels of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin in the brain.
Reduces stress. Tongkat has adaptogenic properties, which means it can help the body adapt to stress by reducing cortisol levels and improving mood. This can lead to improved overall health and wellbeing.
Improves cognitive function. Tongkat ali has been shown to improve memory, concentration, and cognitive function in both healthy individuals and those with cognitive impairments. It works by increasing levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that is essential for the growth and survival of neurons.
Side-effects
It’s important to speak with a healthcare professional before taking tongkat ali if you’re taking any medications.
Tongkat ali can sometimes increase testosterone levels, leading to side-effects like acne, hair loss, and mood swings. The herbal may also interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, antidepressants, and diabetes medications.
Tongkat can cause gastrointestinal side effects like nausea, bloating, and diarrhea in some people. These side effects are usually mild and go away on their own, but if they persist, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional.
Tongkat ali has been shown to increase energy levels, which can make it difficult to sleep if taken too close to bedtime. It’s recommended to take Tongkat Ali earlier in the day to avoid insomnia.
In conclusion, tongkat ali is a popular supplement with numerous potential benefits, including improved libido, athletic performance, mood, and cognitive function.
Due to its popularity, tongkat ali is sometimes adulterated with other substances, which can lead to safety concerns. It’s important to purchase it from a reputable source to ensure purity and safety. Any manufacturer with international certification for their organic products would be a great choice.









