Premium Vitamin B12 Cyanocobalamin 1%: 100g-1kg – Brain & Wellness Support
$25.50 – $88.02Price range: $25.50 through $88.02
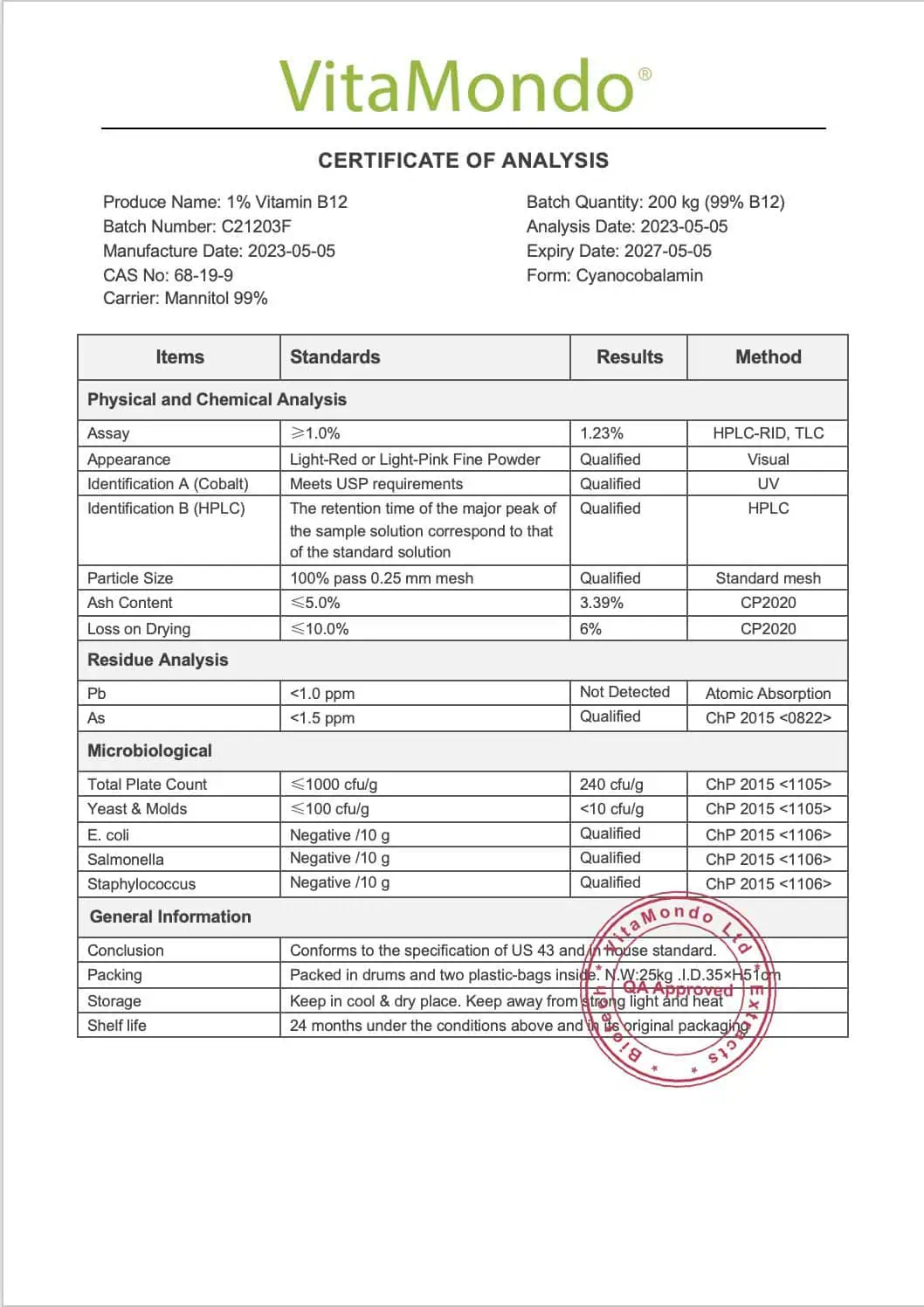
Pure Vitamin B12 Cyanocobalamin 1%
Vitamin B12 – also known as cyanocobalamin in this form – is a water-soluble essential nutrient required for multiple physiological functions, including energy metabolism, red blood cell formation, and nervous system maintenance.
While B12 occurs naturally in animal-derived foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy, it is not typically found in plant-based foods, making it an important supplement for individuals on vegetarian or vegan diets. Modern farming practices and dietary changes also mean that B12 fortification and supplementation are increasingly relevant for the wider population. (In fact, the food that farm animals consume often also has to be fortified.)
Our pure Vitamin B12 Cyanocobalamin 1% is produced from a non-animal source and is suitable for vegetarians. The cyanocobalamin form is stable and well-absorbed, converting efficiently into the biologically active forms methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin in the body.
Key Support Areas
-
Energy Metabolism – Contributes to the normal conversion of food into cellular energy, helping to reduce tiredness and fatigue.
-
Red Blood Cell Formation – Supports the production of normal red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body.
-
Nervous System Function – Plays a role in maintaining healthy nerve signal transmission and myelin integrity.
-
Cognitive Function – Contributes to normal psychological and cognitive performance, including memory and concentration.
-
Homocysteine Metabolism – Helps maintain healthy homocysteine levels, supporting cardiovascular wellness as part of a balanced diet and lifestyle.
-
DNA Synthesis – Required for the normal synthesis of DNA, which underpins cell growth and repair.
-
Mood & Well-Being – Involved in neurotransmitter function, supporting mental and emotional balance.
-
Vegan & Vegetarian Friendly – Provides a reliable source of vitamin B12 for those avoiding animal products.
Suggested Use
Typical daily intake: 25–50 mg of this 1% product (providing 250–500 mcg vitamin B12).
Those with increased needs – such as older adults, pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, or those with certain dietary patterns – may choose higher intakes in consultation with a health professional.
Ingredients
Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin) 1% on mannitol base. Purity of vitamin B12 at manufacturing >99%. Non-animal source. Suitable for vegetarians.
Suggestions
A few products with some similarities are Empty Vegetarian Caps (HPMC), Enteric Coated Capsules, Empty Transparent Gelatin Caps, and Vitamin K2 MK7.
Disclaimer
The various effects are not guaranteed and results may vary due to several factors between different people.
We strive to ensure the accuracy of the information provided by the manufacturers and recommend that you read all labels and warnings. However, the information is not a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Shipping
We are proud to offer international shipping services that currently operate in over 100 countries and islands worldwide.
How do you ship packages?
Packages are shipped by various shippers on the weight and size of the product For more information, see our Shipping & Delivery link at the bottom of any page.
Do you ship worldwide?
Yes. We provide free shipping to over 100+ countries around the world. However, there are some locations we are unable to ship to. If you happen to be located in one of those countries we will contact you.
What about customs?
We are not responsible for any custom fees once the items have shipped. By purchasing our products, you consent that one or more packages may be shipped to you and may get custom fees when they arrive to your country. However, please note that we charge the VAT now for a number of countries in advance, which means you do not need to pay this when the parcel arrive.
How long does shipping take?
Shipping time varies by location. These are our estimates:
| Location | *Estimated Shipping Time |
| United States | 7-28 Business days |
| Canada, Europe | 7-28 Business days |
| Australia, New Zealand | 7-28 Business days |
| Central & South America | 12-35 Business days |
| Asia | 12-35 Business days |
| Africa | 12-40 Business days |
*This doesn’t include our 2-5 day processing time.
Do you provide tracking information?
Yes, you will receive an email once your order ships that contains your tracking information. If you haven’t received tracking info within 5 days, please contact us.
My tracking says “no information available at the moment”.
For some shipping companies, it takes 2-5 business days for the tracking information to update on the system. If your order was placed more than 5 business days ago and there is still no information on your tracking number, please contact us.
Will my items be sent in one package?
For logistical reasons, items in the same purchase will sometimes be sent in separate packages, even if you’ve specified combined shipping.
If you have any other questions, please contact us and we will do our best to help you out.
RETURNS
Order cancellation
All orders can be cancelled until they are shipped. If your order has been paid and you need to make a change or cancel an order, you must contact us within 12 hours. Once the packaging and shipping process has started, it can no longer be cancelled.
Refunds
Your satisfaction is our #1 priority. Therefore, you can request a refund or reshipment for ordered products if:
- If you did not receive the product within the guaranteed time( 45 days not including 2-5 day processing) you can request a refund or a reshipment.
- If you received the wrong item you can request a refund or a reshipment.
- If you do not want the product you’ve received you may request a refund but you must return the item at your expense and the item must be unused.
We do not issue the refund if:
- Your order did not arrive due to factors within your control (i.e. providing the wrong shipping address)
- Your order did not arrive due to exceptional circumstances outside the control of VitaMondo (i.e. not cleared by customs, delayed by a natural disaster).
- Other exceptional circumstances outside the control of
*You can submit refund requests within 15 days after the guaranteed period for delivery (45 days) has expired. You can do it by sending a message on Contact Us page
If you are approved for a refund, then your refund will be processed, and a credit will automatically be applied to your credit card or original method of payment, within 14 days.
Exchanges
If for any reason you would like to exchange your product, perhaps for a different size in clothing. You must contact us first and we will guide you through the steps.
Please do not send your purchase back to us unless we authorise you to do so.
Related products
Heart & Circulatory System
Organic Cat’s Claw Extract Powder: 100g-1kg – Uncaria, Gou Teng
Heart & Circulatory System
Premium Berberine HCL 98%: 100g–1kg – Blood Sugar & Wellness Support
Heart & Circulatory System
Organic Shiitake Mushroom Extract Powder: 100g-1kg – AHCC, Energy Support
Fitness & Bodybuilding
Pure Glucosamine Sulfate Powder 100%: 100g–1kg – Joint & Mobility Support